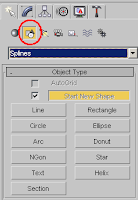
 Splines - one of the most robust tools for advanced modeling.
Splines - one of the most robust tools for advanced modeling.The simple and most widely used is the line, since once you draw it you can modify the vertexes by coordinates.
There are a number of modifying options under the line object.
a) By selecting the line and clicking the modify tab you can adjust each vertex by pressing 1, modify a segment by pressing 2, or the entire spline by pressing 3.
By drawing the simple lines (splines) you can then apply effects to make them 3 dimensional. The following are the most widely used modifiers that are selected from the same modifying tab that the bend/stretch and others were used from the prior lesson:
 1. Extrude-pushes out a shape out of a simple object. To use this, draw any shape using a line or any spline. Next select it, go to modify tab and select the extrude function. The options for this are. Amount is the height by which the object is extruded. Segments indicates the amount of polygon layers applied the extruded surface.
1. Extrude-pushes out a shape out of a simple object. To use this, draw any shape using a line or any spline. Next select it, go to modify tab and select the extrude function. The options for this are. Amount is the height by which the object is extruded. Segments indicates the amount of polygon layers applied the extruded surface.A 3D object can be viewed in skeletal mode by pressing F3, by pressing F3 again it turns back to an opaque form. To show opaque and skeletal overlay press F4.

2. Lather-is another popular modifier, it is very helpful in building glasses, vases and any cylindrical object of various shape. To use it, draw a silhouette of an object you want to rotate around its axis. In this case I made a glass shape. Next, by selecting it find the modifier Lathe and apply.
Degrees specifies if you would like to rotate the object entirely around or a certain amount, in my case it is slightly cut, because the degrees are not 360.
Weld core check box is useful to get rid of bad texturing occurring mostly at the bottom of the rotating object, where there has to be a filled surface.
Flip normals is used when the object appears completely black and no texture appears on it.
Direction indicates along which axis to apply the effect, in my case it is the y-axis.
Finally the Align indicates at which point of the drawn shape to start the rotation, by selecting each option you will understand how it affects the shape.
3. Sweep - is a useful function if you want to quickly apply a shape to a line. In this case I selected a pre-built object, a Bar. But you can apply any shape if you draw it beforehand. Basically this function takes a simple object and draws it along the specified path. By applying your own object, first draw it using splines. Then in the modify click select "Use custom Selection" and click "Pick" and click on your object. That shape will now follow the path of your original object. If you are using the predefined objects, there are a number of options you can modify such as:
Length, Width - varies the length and width parameters of the built-in object (in this case bar)
Corner Radius - smooths the applied object.
The sweep parameters allow modifying the angle and spacing of the object along the chosen path. Hence, X and Y Offset modify the spacing in those directions and the angle twists the object.